
Tantalum – the specialist metal that we carry every day
Not many people have heard of tantalum. After all, it’s just another element that sits somewhere in the periodic table. But did you know, it’s one of the most important metals of the 21st century? The chances are, without even realising it, you carry a piece of tantalum metal around with you every day.
What is tantalum and who discovered it?
Tantalum is a hard, bright, silver metal – characterised by its high melting point, resistance to corrosion and dielectric oxide layer. It’s also extremely ductile, which means it can be easily machined and fabricated into a wide range of tantalum parts and fittings.
Technically speaking, tantalum was first discovered in 1802 by the Swedish chemist, Anders Ekeberg. But the element was questioned by William Wollaston (an English chemist and physicist) – who analysed the minerals from which it was extracted and concluded that it was identical to niobium.
It was only in 1846 that a German mineralogist, Heinrich Rose, looked into the matter further – finally proving that tantalum and niobium are, in fact, two completely separate metal elements.
21st century uses of tantalum
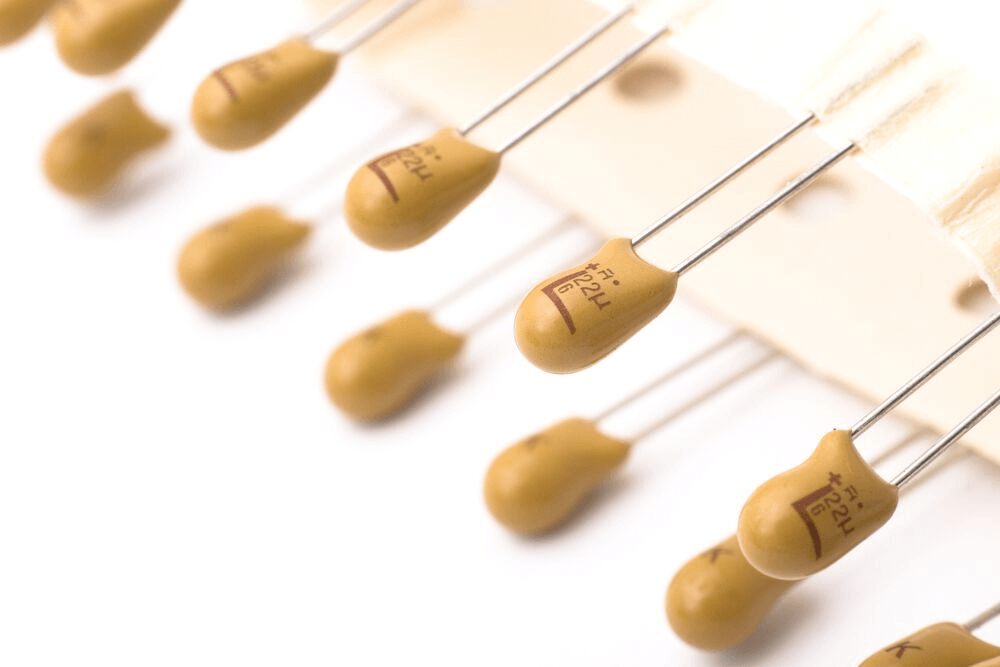
Fast forward over 150 years and tantalum metal has become essential to a wide range of industries. Its primary usage now is within the electronics sector, with over 75% of modern-day electronics containing tantalum in some shape or form – most commonly as a tantalum capacitor.
What is a tantalum capacitor?
Essentially, a tantalum capacitor is a subtype of a standard capacitor – a small electrical device (made from electrical conductors and an insulator) used to store electrical energy. They’re very similar to a battery. When a capacitor is connected to a power source, it accumulates energy, and this energy can later be released when the device is unplugged or disconnected.
Thanks to its unique properties, tantalum is perfectly suited to use as a capacitor. The metal itself acts as the anode (i.e. the electrical conductor), whilst its exterior oxide layer serves well as the dielectric (i.e. the insulator) – creating an exceedingly high capacitance per volume.
How can a tantalum capacitor be used?
As a result of their high capacitance, tantalum capacitors are perfect for use in small electronic devices. For example, they’ve become increasingly seen in mobile phones, especially as manufacturers look to decrease their size and make space for larger processors. Approximately 40mg can now be found in most models.
Tantalum capacitors are also non-toxic and boast an impressively low failure rate. As such, they’re ideal for use in a wide range of medical equipment and devices – including everything from simple hearing aids and orthopaedic implants to an artificial cardiac pacemaker.

Other uses of tantalum metal
Tantalum metal has a wide range of favourable properties; therefore, aside from use as a tantalum capacitor, it’s also suitable for many other industrial applications.
For example, it’s an excellent conductor and is regularly employed for high-temperature applications – such as heating elements and vacuum furnace parts. Tantalum also demonstrates fantastic resistance to corrosion and, as such, is frequently used in chemical processing equipment.
Want to know more about tantalum metal?
Why not get in touch? Special Metals is a leading supplier and manufacturer of tantalum and tantalum metal parts. Our team have expert knowledge of this popular material and can provide further information on its properties, uses and how it could be of benefit to you. Either give us a call today on +86-755-29936699 or send an email to inquiry.mp@professionalmanufacturing.com and we’ll get back to you.

Leave a response
Your email address will not be published. Please enter your name, email and a comment.